LeetCode DP(中)
本篇是LeetCode DP类别的中级(Medium(前四) + Hard)题目:
- Unique Paths
- Unique Paths II
- Unique Binary Search Trees
- Unique Binary Search Trees II
- Edit Distance
- Distinct Subsequences
- Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
- Longest Valid Parentheses
#1.Unique Paths ref
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked ‘Start’ in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked ‘Finish’ in the diagram below).
How many possible unique paths are there?
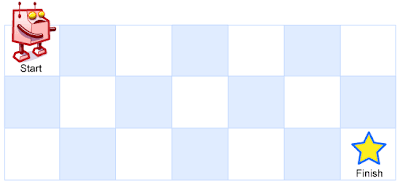
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
- pathNum[i][j]表示(0,0)到(i,j)的不同路径数目,递推关系如下
pathNum[i][0] = 1;
pathNum[0][i] = 1;
pathNum[i][j] = pathNum[i - 1][j] + pathNum[i][j - 1];
int uniquePaths(int m, int n)
{
vector<vector<int>> pathNum(m, vector<int>(n));
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
pathNum[i][0] = 1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
pathNum[0][i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++)
{
pathNum[i][j] = pathNum[i - 1][j] + pathNum[i][j - 1];
}
}
return pathNum[m - 1][n - 1];
}#2.Unique Paths II ref
Follow up for “Unique Paths”:
Now consider if some obstacles are added to the grids. How many unique paths would there be?
An obstacle and empty space is marked as 1 and 0 respectively in the grid.
For example,
There is one obstacle in the middle of a 3x3 grid as illustrated below.
[
[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,0]
]
The total number of unique paths is 2.
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
- pathNum[i][j]表示(0,0)到(i,j)的不同路径数目,递推关系如下
pathNum[0][0] = obstacleGrid[0][0] == 0? 1:0;
pathNum[0][i] = obstacleGrid[0][i] == 0? pathNum[0][i-1]:0;
pathNum[i][0] = obstacleGrid[i][0] == 0? pathNum[i-1][0]:0;
pathNum[i][j] = obstacleGrid[i][j] == 0? pathNum[i - 1][j] + pathNum[i][j - 1] : 0;
int uniquePathsWithObstacles(vector<vector<int> > &obstacleGrid)
{
int m = obstacleGrid.size();
int n = obstacleGrid[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> pathNum(m, vector<int>(n, 0));
if (obstacleGrid[0][0] == 0){
pathNum[0][0] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++){
if (obstacleGrid[i][0] != 1){
pathNum[i][0] = pathNum[i - 1][0];
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++){
if (obstacleGrid[0][i] != 1){
pathNum[0][i] = pathNum[0][i - 1];
}
}
//other grid
for (int i = 1; i < m; i++){
for (int j = 1; j < n; j++){
if (obstacleGrid[i][j] != 1){
pathNum[i][j] = pathNum[i - 1][j] + pathNum[i][j - 1];
}
}
}
return pathNum[m - 1][n - 1];
}#3.Unique Binary Search Trees ref
Given n, how many structurally unique BST’s (binary search trees) that store values 1…n?
For example,
Given n = 3, there are a total of 5 unique BST’s.
1 3 3 2 1
\ / / / \ \
3 2 1 1 3 2
/ / \ \
2 1 2 3
####思路
- 由1,2,…,n构成的BST总数 f(n) = 1为根的BST 个数 + 2为根的BST 个数 + … + n为根的BST 个数
- 由1,2,…,n构成的以k(1=<k<=n)为根的BST总数 g(n,k) = f(k-1) * f(n-k)
- 根k的左子树包含1,2,…,k-1,根k 不同的左子树数目是f(k-1);
- 根k的右子树包含k+1,k+2,…,n,它和包含1,2,…,n-k表示的子树同构,所以不同的右子树数目为f(n-k);
- 根据乘法原理得 g(n,k) = f(k-1) * f(n-k)
- f(n) = g(n,1)+g(n,2)+,…,+g(n,n)
int numTrees(int n)
{
assert(n > 0);
vector<int> f(n + 1, 0);
f[0] = 1;
f[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{//f(i)
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{//g(i,j)
f[i] += f[j - 1] * f[i - j];
}
}
return f[n];
}#4.Unique Binary Search Trees II ref
Given n, generate all structurally unique BST’s (binary search trees) that store values 1…n.
For example, Given n = 3, your program should return all 5 unique BST’s shown below.
1 3 3 2 1
\ / / / \ \
3 2 1 1 3 2
/ / \ \
2 1 2 3
DFS方法构造BST
class Solution {
vector<TreeNode *> buildBST(int start, int end)
{
vector<TreeNode*> subtree;
if (start > end)
{
subtree.push_back(NULL);
return subtree;
}
if (start == end)
{
TreeNode *node = new TreeNode(start);
subtree.push_back(node);
return subtree;
}
for (int i = start; i <= end; i++)
{
TreeNode *root;
vector<TreeNode*> vleft = buildBST(start, i - 1);
vector<TreeNode*> vright = buildBST(i + 1, end);
for (int j = 0; j < vleft.size(); j++)
{
for (int k = 0; k < vright.size(); k++)
{
root = new TreeNode(i);
root->left = vleft[j];
root->right = vright[k];
subtree.push_back(root);
}
}
}
return subtree;
}
public:
vector<TreeNode *> generateTrees(int n)
{
return buildBST(1, n);
}
};#5.Edit Distance ref
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of steps required to convert word1 to word2. (each operation is counted as 1 step.)
You have the following 3 operations permitted on a word:
a) Insert a character
b) Delete a character
c) Replace a character
这是动态规划的一个经典题目,下面用一个例子说明求解思路
- 用dist[i][j]表示string1[0…i-1]转换成string2[0…j-1]所需的最少步骤
- 若 s1[i - 1] == s2[j - 1]
- dist[i][j] = min(min(dist[i - 1][j], dist[i][j - 1]) + 1, dist[i - 1][j - 1]);
- 否则 dist[i][j] = min(min(dist[i - 1][j], dist[i][j - 1]) + 1, dist[i - 1][j - 1] + 1);
一图胜千言,从word转换成world的步骤如下图所示:

int minDistance(string s1, string s2)
{
int m = s1.size();
int n = s2.size();
vector<vector<int> > dist(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));
for (int i = 0; i <= m; i++)
{//delete
dist[i][0] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
{//insert
dist[0][i] = i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
if (s1[i - 1] == s2[j - 1])
{
dist[i][j] = min(min(dist[i - 1][j], dist[i][j - 1]) + 1, dist[i - 1][j - 1]);
}
else
{
dist[i][j] = min(min(dist[i - 1][j], dist[i][j - 1]) + 1, dist[i - 1][j - 1] + 1);
}
}
}
return dist[m][n];
}#6.Distinct Subsequences ref
Given a string S and a string T, count the number of distinct subsequences of T in S.
A subsequence of a string is a new string which is formed from the original string by deleting some (can be none) of the characters without disturbing the relative positions of the remaining characters. (ie, “ACE” is a subsequence of “ABCDE” while “AEC” is not).
Here is an example:
S = “rabbbit”, T = “rabbit”
Return 3.
它和Edit Distance很相似
- 用path[i][j]表示T[0…i]在S[0…j]中的不同子序列数
- path[0][i] = 1; ““在S[0…i]中的不同子序列数为1
- path[i][0] = 0; T[0…i]在”“中的不同子序列数为0
- Path[i][j] = Path[i][j-1] //discard S[j]
-
- Path[i-1][j-1] //S[j] == T[i] and we are going to use S[j]
- or 0 //S[j] != T[i] so we could not use S[j]
-
int numDistinct(string S, string T)
{
int n = S.length();
int m = T.length();
if (m > n)
return 0;
vector<vector<int>> path(m + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));
for (int k = 0; k <= n; k++)
path[0][k] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
{
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
path[i][j] = path[i][j - 1] + (T[i - 1] == S[j - 1] ? path[i - 1][j - 1] : 0);
}
}
return path[m][n];
} #7.Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III ref
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete at most two transactions.
Note: You may not engage in multiple transactions at the same time (ie, you must sell the stock before you buy again).
Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock最多交易一次,本题目多了一次交易,可以买卖2次,思路就是这个2,难点就是在两次交易不重叠的情况下获得最大收益:
- g(i)表示第0天到第i天交易一次的最大收益,计算方法和Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock一样;
- f(i)表示第i天到第n天交易一次的最大收益;
- 这样当求g(i)+f(i)的最大值时就不会出现交易重叠的情况了。
int maxProfit(vector<int> &prices)
{
int n = prices.size();
if (n < 2){
return 0;
}
vector<int> g(n, 0);
vector<int> f(n, 0);
for (int i = 1, minP = prices[0]; i < n; i++){
minP = min(minP, prices[i]);
g[i] = max(g[i - 1], prices[i] - minP);
}
for (int i = n - 2, maxP = prices[n - 1]; i >= 0; i--){
maxP = max(maxP, prices[i]);
f[i] = max(f[i + 1], maxP - prices[i]);
}
int max_profit = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++){
if (max_profit < g[i] + f[i]){
max_profit = g[i] + f[i];
}
}
return max_profit;
}#8.Longest Valid Parentheses ref
Given a string containing just the characters ‘(‘ and ‘)’, find the length of the longest valid (well-formed) parentheses substring.
For “(()”, the longest valid parentheses substring is “()”, which has length = 2.
Another example is “)()())”, where the longest valid parentheses substring is “()()”, which has length = 4.
Stack is used to stored the character.
If current character is ‘(‘, push into the stack. If current character is ‘)’, Case 1: the stack is empty, reset previous result to zero. Here we renew a pointer to store the earliest index. Case 2: the stack is not empty, pop the top element. if the top element is ‘(‘ , (which means a () pair is found), then if the poped stack is empty, (which means the previous pairs should be added.), len = current pos - previous pos +1; If the poped stack is not empty, len = current pos- index of stack top element.
####思路
- 通常的括号匹配,一般用stack来保存左括号,遇到右括号就弹出一个字符进行匹配;本题只有’(‘,’)’,所以保存’(‘和保存任意内容都是一样的;
- 用stack保存’(‘在string中的位置;
- 用last记录上一次不匹配的字符串位置,初始last = -1
- 遍历string s,如果s[i]==’(‘,就压入i;
- 如果s[i]==’)’:
- 如果栈为空,说明匹配失败, last = i; 如())()
- 否则弹出一个元素,然后再判断栈是否为空?
- 如果栈为空,说明s[last+1…i]全部匹配,并且可能向下连续; 如()()(), maxlen = max(maxlen, i - last);
- 否则可能出现嵌套,如(()())(), 先求出现当前最大长度 maxlen = max(maxlen, i - sp.top());
int longestValidParentheses(string s)
{
if (s.size() < 2){
return 0;
}
stack<int > sp;
int maxlen = 0;
int last = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < s.size(); i++){
if (s[i] == '('){
sp.push(i);
}
else{
if (sp.empty()){//not match
last = i;
}
else{
sp.pop();
if (sp.empty()){
maxlen = max(maxlen, i - last);
}
else{
maxlen = max(maxlen, i - sp.top());
}
}
}
}
return maxlen;
}
留下评论